How to Invest in Share Market in India: Beginners Guide 2025

The Indian share market is full of opportunities for those who are ready to learn and take smart steps. While not every investment gives instant returns, with the right knowledge and planning, you can increase your chances of success. Again, you don’t need to be an expert to begin. What you need is clear guidance and a little patience. The most important step is to stop relying only on tips or suggestions. Instead, take time to understand how to invest in share market the right way.
This blog will help you take that first step with confidence.
What is the Share Market?
The share market is a platform where investors can buy and sell shares of publicly listed companies. By purchasing shares, investors own a portion of that company. If the company performs well, shareholders may benefit from capital appreciation (increase in share value) and dividends (a portion of profit distributed to shareholders).
Why do companies issue shares?
Companies issue shares to raise money from the public or investors. This money helps them grow their business, launch new products, repay debts, or expand into new markets. Instead of taking a loan, they offer ownership of the company through shares. In return, investors get a chance to earn profits through dividends or price growth.
Types of Share Markets
1. Primary Market:
This is where new shares or securities are first offered to investors.
2. Secondary Market:
Here, investors buy and sell shares or securities from each other, not from the company directly.
In India, the two primary stock exchanges are:
- Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE)
- National Stock Exchange (NSE)
These exchanges are regulated by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
How to Invest in Share Market in India
In India, you can invest in different securities like shares, bonds, mutual funds, ETFs, etc. Shares give you part ownership in a company. Bonds are like loans you give to companies or the government, mutual funds pool money to invest in many assets, and ETFs trade like stocks but give you diversification.
Each has its own benefits and risks.
Here is the step-by-step guide to start investing in India-
1. Opening a Demat and Trading Account
Investing in stocks requires two essential accounts:
- Demat Account- It holds shares in electronic form.
- Trading Account– This enables the buying and selling of shares on the stock exchange.
These accounts can be opened with a SEBI-registered stock broker. Most brokers offer integrated Demat and trading account services.
2. Linking a Bank Account
A bank account must be linked to the trading account to transfer funds in and out during the investment process.
3. Completing KYC (Know Your Customer)
KYC compliance is mandatory. Investors must submit identity proof, address proof, a recent photograph, and PAN card details. Aadhaar-PAN linking is also required as per SEBI regulations.
4. Understanding Basic Market Concepts
Before trading, beginners should learn:
- Stock types (large-cap, mid-cap, small-cap)
- Market orders (buy/sell orders at current market prices)
- Limit orders
- Market segments- bonds, mutual funds, IPOs, ETFs, currencies, commodities, etc.
5. Research Before Investing
Study company performance by reading financial news and keeping an eye on stock charts.
6. Start Small, Grow Slowly
Pick one or two well-known companies to begin with. Invest in small amounts and track how they perform.
Key Stock Market Terms for Beginners
Here are a few terms you must know if you are yet to kickstart your stock market investment journey.
1. IPO (Initial Public Offering) – This is when a company offers its shares to the public for the very first time.
2. P/E Ratio (Price-to-Earnings Ratio) – This shows how much investors are willing to pay for each rupee of a company’s earnings. A higher P/E could mean high growth expectations.
3. Dividends – These are payments companies give to shareholders from their profits. It’s like a reward for owning their stock.
4. Market Cap (Market Capitalization) – The total value of all a company’s shares combined. It helps you understand the company’s size.
5. ETF (Exchange-Traded Fund) – A bundle of stocks or assets you can buy or sell together, just like a single stock.
6. SIP (Systematic Investment Plan) – A method of investing small amounts regularly in mutual funds, perfect for beginners.
7. Bull Market – When stock prices are generally rising, creating positive investor sentiment.
8. Bear Market – When stock prices are falling, leading to a cautious or negative outlook.
9. Liquidity – How quickly you can buy or sell an investment without affecting its price.
10. Brokerage – The fee you pay to a broker or platform when you buy or sell stocks.
When to Buy and Sell Stocks
Buying low, selling high. Let’s learn the best moments to jump in and cash out in the stock market!
Buying Stocks: Best Practices
Buying a stock means you’re putting your money into a company because you believe it will grow in the future. But how do you decide when to invest?
Here are some simple situations when buying may be a good idea:
1. After Proper Research
Don’t buy just because a friend told you it’s a “hot stock.” Instead, check:
- What does the company do?
- Is it earning regular profits?
- Is the industry growing?
2. During Market Corrections
Sometimes the overall market falls due to news, elections, or global events. Even strong companies’ share prices drop during such times. These can be good chances to invest.
3. When the Company Shows Growth Signs
If a company is expanding, launching new products, or entering new markets, it may grow in value.
Selling Stocks: Strategic Triggers
Selling a stock is just as important as buying it. Knowing when to exit helps protect your profits and avoid big losses.
1. You’ve Reached Your Goal
If your stock has grown and helped you reach your financial target, it’s okay to sell.
2. The Company’s Performance is Falling
If you notice that the company’s profits are going down or it’s getting negative news, you may consider selling.
3. The Stock is Overvalued
Sometimes, a stock’s price increases too fast and reaches a level higher than its actual worth. Experts call this “overvaluation.” If this happens, you can sell and book profits.
4. You Need the Money
Life is unpredictable. If you need urgent money for a medical emergency, home repair, or education, it’s okay to sell your stocks — even if you plan to hold them longer.
Try to avoid panic selling just because prices dropped in one day. Only sell if it fits your real need or long-term plan.
How Much Should You Invest as a Beginner?
You don’t need a lot of money to start investing. Even ₹500 to ₹2,000 a month is enough if you go with a mutual fund SIP.
Or, you could also buy a couple of good stocks to begin with. What matters most is getting started. It is not about how much you invest.
Start small, and stay regular!
Investment Strategies for Beginners
Investing in the share market is a great way to grow your money. But it’s important to start right.
Learn the basics!
1. Long-Term Investing
Holding quality stocks for 5–10 years can help build wealth gradually. This strategy reduces the impact of short-term market volatility.
2. Systematic Investment in Stocks
Similar to mutual fund SIPs, investors can allocate a fixed amount monthly to purchase stocks, averaging the cost over time.
3. Diversified Portfolio Approach
Investing across sectors (e.g., banking, healthcare, IT, pharma) reduces risk by avoiding overexposure to a single industry.
4. Blue-Chip Stock Focus
You should begin with well-established companies with stable earnings, strong balance sheets, and a long operating history.
Start Investing Right: Learn About Risks First
Before you start investing in the stock market, it’s important to know your goals and how much risk you can take.
Important Risks to Keep in Mind
- Market Risk: Sometimes, the whole market or economy can slow down, which can cause losses.
- Inflation Risk: Inflation means prices go up, so your money might lose value over time.
- Liquidity Risk: You may not always be able to sell your investment quickly when you want to.
- Business Risk: The company you invest in could face problems or even stop running.
- Volatility Risk: Stock prices can move up and down a lot, which can be risky.
- Currency Risk: If you invest in foreign stocks or currencies, changes in exchange rates can cause losses.
One simple way to protect your investments is to spread your investments across different companies and types of assets. This helps reduce risk and keeps your money safer.
Think stocks are a shortcut to quick money? Think again.
One smart move can grow your wealth, and one wrong step can cost it.
Let’s understand the simple do’s and don’ts every investor must know.
New to investing? read our guide on Setting the Right Financial Goals Can Change Your Life—Here’s How!
Stock Market Investing: Know Your Rights & Responsibilities
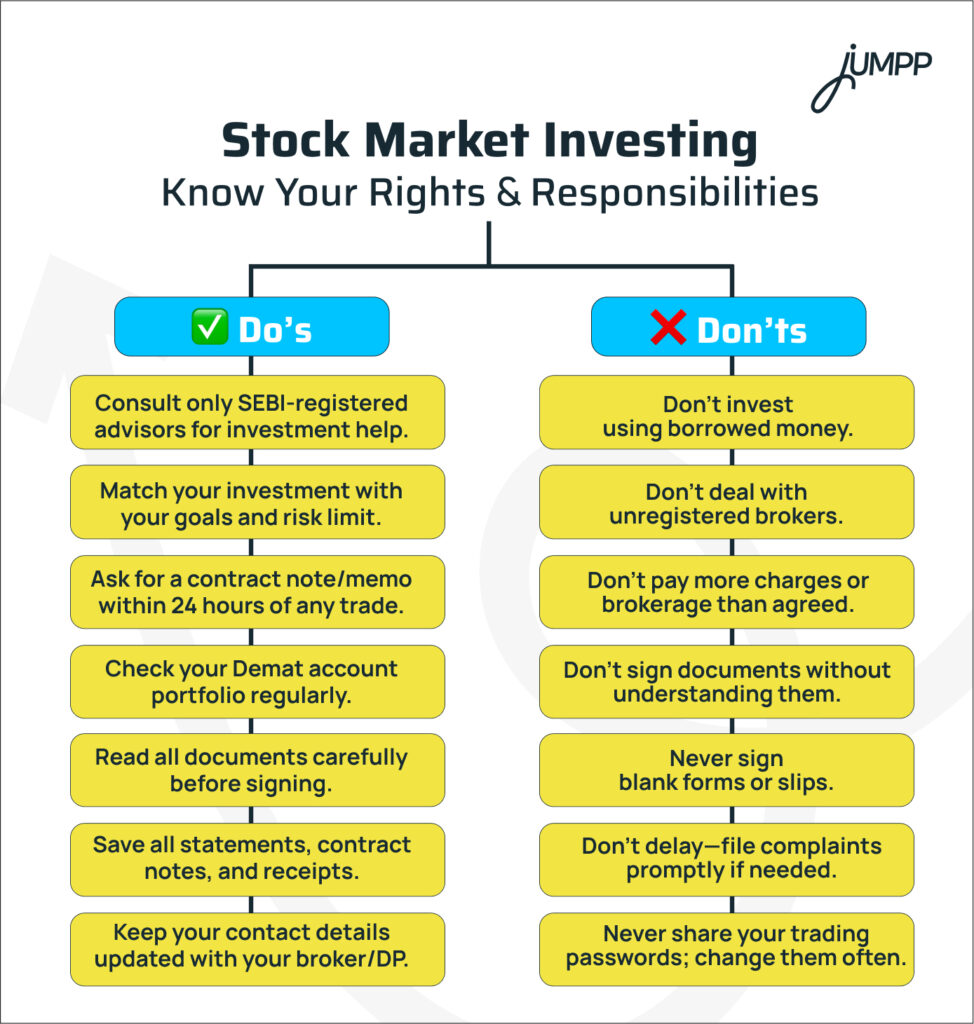
Don’t Lose Money to These Common Investing Errors!
New to stock market investing? Mistakes are common but avoidable.
Many beginners lose money not because of bad stocks but bad habits.
Here are the most common pitfalls you should be aware of-
- Chasing Penny Stocks: Low-priced stocks can be risky due to poor fundamentals.
- Overtrading: Frequent buying and selling can erode gains due to brokerage and tax costs.
- Ignoring Taxation: Understand capital gains tax.
Short-term (within 1 year) is taxed at 15%, while long-term gains (after 1 year) above ₹1 lakh are taxed at 10%.
- Lack of Discipline: Emotional decisions, especially during market volatility, often result in losses.
From stocks to SIPs, ETFs to Mutual Funds, it’s all here.
Invest smarter and faster with jUMPP!
Conclusion
Investing in the stock market can be a great journey when approached with proper knowledge, discipline, and patience.
Stock brokers play a critical role in this journey by offering tools, research, and platforms that help investors trade efficiently.
The key to success lies not in timing the market but in time spent in the market. With continuous learning and the right support, any beginner can become a confident and capable investor.
How to Invest in Share Market: FAQs
To invest in the share market, you need a Demat and trading account. Once you have these, you can buy and sell shares through stock exchanges like NSE or BSE.
Beginners start by opening a Demat account and learning about shares. They usually begin with small investments to understand the market.
The best time depends on market conditions and your goals. Many investors watch price trends and company news before making decisions.
Beginners often focus on learning the basics, researching companies, and avoiding quick decisions based on rumours.
Beginners invest by buying shares of companies through a broker. They can track their investment using their Demat account.
Investors buy or sell stocks based on their financial goals, market trends, and company performance, but timing can vary widely.
New investors usually learn the stock market basics, research well, avoid rumours, and keep track of their investments regularly.
You’ll need a PAN card, an Aadhaar, a bank account, and proof of address to open a Demat and trading account.




