Don’t Buy Health Insurance Without Knowing the Coinsurance Meaning

When most people in India think about health insurance, they imagine complete financial protection during a medical emergency. The assumption is simple. You pay the premium, and the insurer will cover the hospital bill in full. But in practice, it is different. You paid the premium, so why are you still paying at the hospital? One of the lesser-known but crucial aspects of a health insurance policy is coinsurance. If you’re wondering about coinsurance meaning, it refers to the percentage of the medical bill that you, the policyholder, are required to pay after the deductible is met.
In this article, we will introduce you to the overall concept of coinsurance in India!
What is Coinsurance?
Coinsurance means cost-sharing between you and the insurance company. After you’ve paid your deductible (the fixed amount you pay first), you and your insurer split the remaining costs in a fixed percentage.
Let us say that you have a 20% coinsurance.
Your total bill is ₹1,00,000.
You’ve already paid your deductible.
Now, you’ll pay ₹20,000 (20%), and your insurer pays ₹80,000 (80%).
What is Coinsurance in Medical Billing?
In medical billing, coinsurance works the same way, but it’s used more specifically to calculate how much the patient owes after treatment, based on their health insurance plan.
It’s part of the billing structure hospitals and clinics use to decide:
- What amount to bill the insurance
- What amount to bill the patient (you)
In health insurance, coinsurance refers to the fixed percentage of the treatment cost that you, the policyholder, are required to pay after your insurance deductible has been met. The remaining cost is paid by the insurance company.
When you take out insurance, you and your insurer share the bill. Your part of the share is called coinsurance.
The percentage is usually defined at the time of buying the policy. It can be 10 percent, 20 per cent, or more, depending on the plan structure.
Let us understand the Coinsurance Meaning with an Example
Let’s say you have a health insurance policy with 20 percent coinsurance. You are hospitalised for surgery, and the final bill comes to ₹1,00,000.
Now, assume you’ve already paid your deductible (we’ll come to that in a moment).
Out of the ₹1,00,000, you are required to pay 20 percent, which is ₹20,000. The insurer will pay the remaining 80 percent, or ₹80,000.
That ₹20,000 is your coinsurance. It’s not a penalty or a hidden fee. It’s part of the contract you agreed to when you bought the policy.
What is a Deductible in Health Insurance?
A deductible is the amount of money you must pay from your own pocket before your health insurance starts helping you with the rest of the bill.
Your health insurance is a safety cover, but it doesn’t cover you immediately. First, you have to pay a certain amount. That amount is called the deductible.
Explore the different types of health insurance in India
Let’s take an example.
Suppose your health insurance has a deductible of ₹10,000. If you get hospitalised and the total bill comes to ₹80,000, you will first pay ₹10,000. Only after that will the insurance company step in and pay the remaining ₹70,000 (depending on other terms like coinsurance or copay).
In India, many health policies, especially top-up or super top-up plans, include deductibles. It helps reduce the premium cost, but you must be ready to pay from your pocket when a claim happens.
So in simple terms:
- Deductible is the first expense.
- It is paid by you before the insurer covers the rest.
- The higher the deductible, the lower your premium, but the more you pay during hospitalisation.
If you’re healthy and want to reduce your premium, a higher deductible policy might make sense. But if you want full financial protection, you can choose a policy with a low or zero deductible.
What is Copayment in Health Insurance?
Now let’s talk about copayment, also known as copay. This is another type of cost-sharing between you and your insurer, but it works differently from a deductible.
A copayment is a fixed amount that you agree to pay every time you use a specific medical service, such as hospitalisation, doctor visits, or diagnostic tests. It doesn’t matter what the total bill is. The copay amount remains the same.
For example, if your policy has a ₹1,000 copay for every hospitalisation, then:
- Whether the total bill is ₹25,000 or ₹2,50,000, you still pay ₹1,000.
- The insurer pays the rest, depending on your policy terms.
Some Indian health policies include copay clauses for:
- Senior citizens
- Non-network hospitals
- OPD treatments
- Group insurance policies
So what’s the point of a copay? Insurance companies add it to encourage responsible use of healthcare. When people know they have to pay a fixed amount, they avoid unnecessary treatments. For the insurer, it helps reduce small claims.
In short:
- Copayment is a fixed amount.
- You pay it every time you use a service.
- It is separate from and may apply even after the deductible.
What is the Difference Between Coinsurance and Copayment
Many people think coinsurance and copayment are the same. But they’re not. The difference lies in how much you pay and how it is calculated.
Coinsurance is a percentage of the total medical bill that you agree to pay.
Copayment is a fixed amount you pay every time you use a medical service.
Let’s say you are admitted to the hospital and the final bill is ₹1,00,000.
Now assume:
- Your policy has 20% coinsurance
- And also has a ₹1,000 copay
Here’s how your payment would look:
- You first pay the deductible if your policy has one.
- Then, you pay ₹20,000 (which is 20 percent of ₹1,00,000) as coinsurance.
- On top of that, you also pay ₹1,000 as a copay.
So your total out-of-pocket expense is ₹21,000, plus any deductible if applicable.
In real life, most policies include either coinsurance or copay, not always both. But knowing the difference helps you understand how your medical expenses will be split between you and the insurer.
Deductible vs Copay vs Coinsurance: What’s the Real Difference in Health Insurance
Let’s put everything together so you can clearly see how these three terms work differently.
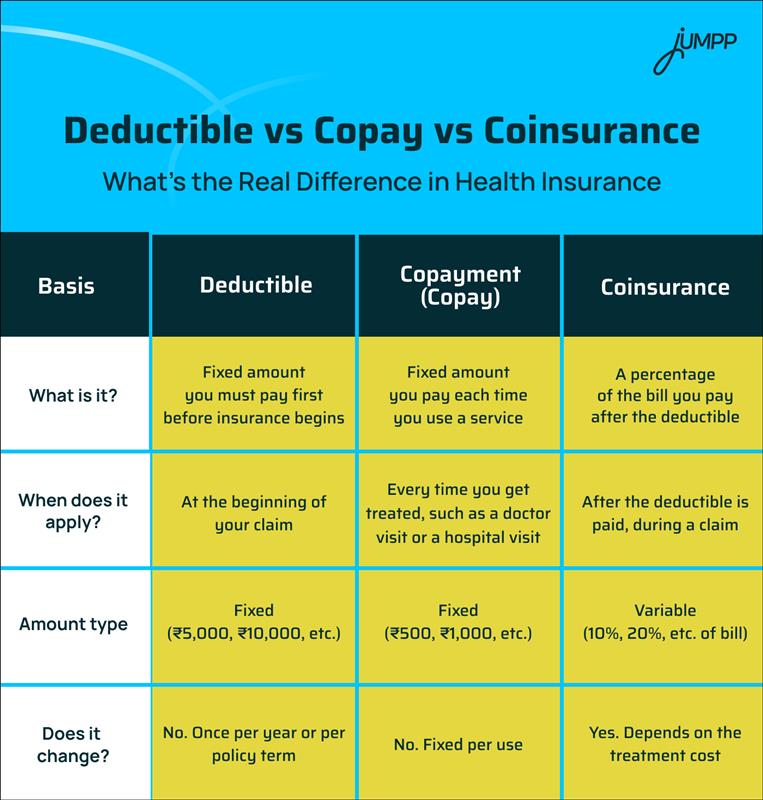
Summary:
- Deductible is the first amount you pay, once.
- A copayment is a small fixed charge per use, no matter the bill.
- Coinsurance is your share of the remaining bill, calculated as a percentage.
How Coinsurance Works in India: Network vs Non-Network Hospitals
In India, most health insurance companies have a list of hospitals where you can get cashless treatment. These are called network hospitals. When you choose a network hospital, the insurer settles the bill directly with the hospital, and you only need to pay your part (like deductible, copay, or coinsurance).
But if you go to a non-network hospital, you may have to pay the entire bill upfront and later file for reimbursement. This is where coinsurance becomes even more important.
Some policies have different coinsurance rates depending on where you get treated.
For example:
- In a network hospital, your coinsurance might be 10 percent.
- In a non-network hospital, the same policy may ask you to pay 20 percent.
Step-by-Step Flow: How Coinsurance Works in Practice
Let’s understand coinsurance with a clear sequence. Here’s how a typical claim works:
- You get hospitalised.
- The total hospital bill is ₹1,50,000.
- Your policy has a deductible of ₹10,000, a coinsurance of 20 percent, and an out-of-pocket max of ₹1,00,000.
- First, you pay the deductible of ₹10,000.
- The remaining bill is ₹1,40,000.
- Then, you pay 20 percent of ₹1,40,000, which is ₹28,000.
- The insurer pays the remaining ₹1,12,000.
- Your total out-of-pocket expense in this case is ₹38,000.
If another hospitalisation happens in the same year:
- You won’t need to pay the deductible again.
- You’ll only pay coinsurance until your total personal expense reaches ₹1,00,000.
- After that, the insurer pays the full amount.
This is how coinsurance works—layered but manageable.
What Happens After You Reach Your Coinsurance Limit?
Once your total payments through deductibles, copays, and coinsurance add up to a set amount called the out-of-pocket maximum, you stop paying. From that point till the end of the policy year, your insurer covers 100 percent of all approved medical costs. Whether it is another hospitalisation or follow-up treatment, you will not have to pay anything extra. This limit gives you financial relief during serious or repeated health issues. It acts as a final safety cap on your personal medical expenses.
Why Do Indian Insurers Use Coinsurance?
Coinsurance is used by insurers for a few reasons.
- To manage risk.
If policyholders know they must pay a part of the bill, they are more likely to avoid unnecessary or overpriced treatments. - To reduce small and frequent claims.
Coinsurance discourages people from making a claim for minor expenses. - To control premium costs.
By adding coinsurance, insurers can offer lower premiums while still protecting against major medical events. - To share responsibility.
Especially for senior citizens or in high-risk categories, coinsurance helps balance the cost between the policyholder and the insurer.
In short, coinsurance is a tool used by insurers to keep plans sustainable while still offering meaningful protection.
Pros and Cons of Coinsurance
Here’s a quick overview of the benefits and limitations of coinsurance:
Pros
- Helps reduce premium cost
- Encourages careful and responsible use of medical services
- Often comes with a cap (out-of-pocket max), which limits financial risk
- Makes high-value health plans more affordable
Cons
- Can lead to high expenses during medical emergencies
- May confuse new policyholders due to technical terms
- Coinsurance rate may vary for network vs non-network hospitals
- Requires policyholders to maintain emergency funds
So, while coinsurance has some benefits, it is not suitable for everyone.
What is Coinsurance, Copay, and Deductible? Explained Together
Imagine your hospital bill is ₹1,00,000.
Here’s what happens if your policy includes:
- Deductible: ₹10,000
- Coinsurance: 20 percent
- Copay: ₹1,000 per hospitalisation
Now, your expenses look like this:
- First, you pay the deductible of ₹10,000
- Next, you pay 20 percent of the remaining ₹90,000, which is ₹18,000
- Then, you add the copay of ₹1,000
- Your total payment: ₹29,000
- The insurer pays the rest: ₹71,000
Should You Choose a Policy with Coinsurance?
It depends on your financial goals and risk comfort.
You may choose coinsurance if:
- You are young and healthy
- You rarely visit hospitals
- You want to save on premium and don’t mind paying a share during a rare emergency
You should avoid coinsurance if:
- You have a family with senior members or chronic health issues
- You want full coverage, even if it means a higher premium
The decision should come down to what you value more—lower premium now or lower expenses later during a claim.
Final Checklist Before Buying Health Insurance
Before buying a policy, make sure you ask these questions:
- What is the coinsurance percentage, and when does it apply?
- Is there a deductible? If yes, how much?
- Does the policy include a copayment?
- What is the out-of-pocket maximum?
- Are the rates different for network vs non-network hospitals?
- Does the coinsurance apply per claim or per policy year?
- Does the policy cover OPD or just hospitalisation?
This checklist helps you look beyond the premium and coverage amount. It helps you see the real cost of using the policy when you need it.
Final Thoughts
Coinsurance is not just an insurance term. It directly affects how much you pay during a medical emergency. And in a country like India, where healthcare costs are rising and hospital bills can vary widely, knowing how your policy works is crucial.
When you choose health insurance, don’t just look at the coverage amount or how low the premium is. Ask yourself:
- What happens during a claim?
- How much do I really pay from my pocket?
Remember, insurance is not just about affordability. It is about assurance.
Coinsurance Meaning: FAQs
Coinsurance means you share a part of the medical bill with your insurer after the deductible is paid. It’s usually shown as a percentage like 10% or 20%.
It means your insurer will pay 80% of the eligible claim amount. You will pay the remaining 20% out of pocket.
Coinsurance is a percentage of the bill you pay, while a copay is a fixed amount per service. Both are cost-sharing clauses, butthey work differently.
A deductible is a fixed amount you must pay first before the insurer pays anything. Coinsurance applies after that, based on the remaining bill.
This is the maximum amount you may need to pay as coinsurance in a policy year. After this, the insurer pays 100% of the remaining covered costs.
If your policy has a ₹1,000 copay per hospital visit, you always pay ₹1,000, whether the total bill is ₹10,000 or ₹1,00,000.
Coinsurance, copay, and deductible are all cost-sharing terms in health insurance. A deductible is what you pay first. A copay is a fixed fee per service. Coinsurance is the percentage you split with the insurer after the deductible is paid.






